 Home
Home
 Back
Back
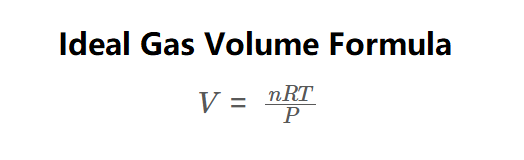
Definition: This calculator computes the volume (\( V \)) of an ideal gas using the ideal gas law, as shown in the formula image above. Volume is calculated via:
\( V = \frac{nRT}{P} \)
Users input pressure (\( P \)), amount of substance (\( n \)), and temperature (\( T \)), with support for multiple units. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places for precision, in units such as m³, cm³, L, cu ft, or cu in.[](https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/ideal-gas-volume)Purpose: Essential for thermodynamics, chemical engineering, and physics to determine gas volume in systems like reactors, balloons, or atmospheric studies.
The calculator uses the ideal gas law (\( PV = nRT \)), rearranged to solve for volume:
\( V = \frac{nRT}{P} \)
Where:
Common Gases and Molecular Masses (for Reference):
| Gas | Molecular Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|
| Air | 28.96 |
| Nitrogen | 28.02 |
| Oxygen | 32.00 |
| Carbon Dioxide | 44.01 |
| Methane | 16.04 |
Steps:
Gas volume calculations are critical for:
Example 1: Calculate the volume of 1 mol of gas at 1 atm and 25°C, with \( R = 8.31446261815324 \, \text{J/(mol·K)} \), output in m³ and L:
Results:
Example 2: Calculate the volume of 0.5 mol of gas at 100 kPa and 77°F, output in cm³ and cu ft:
Results:
Q: What is the ideal gas law?
A: The ideal gas law (\( PV = nRT \)) relates pressure, volume, amount of substance, and temperature for an ideal gas, assuming no intermolecular forces and elastic collisions.
Q: Why use Kelvin for temperature?
A: Kelvin is an absolute scale, ensuring positive temperatures for accurate calculations.
Q: Can this calculator be used for real gases?
A: Yes, for low pressures and high temperatures where real gases approximate ideal behavior. For high pressures, consider the van der Waals equation.
Q: What is the universal gas constant?
A: The universal gas constant (\( R \)) is 8.31446261815324 J/(mol·K), relating energy to temperature and moles in the ideal gas law.
Q: How do I convert between volume units?
A: Use the output unit dropdown to instantly convert volume to m³, cm³, L, cu ft, or cu in.