 Home
Home
 Back
Back
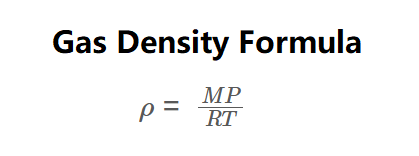
Definition: This calculator computes the density (\( \rho \)) of an ideal gas, defined as mass per unit volume (\( \rho = \frac{m}{V} \)), using the ideal gas law. As shown in the formula image above, density is calculated via:
\( \rho = \frac{MP}{RT} \)
Users input pressure (\( P \)), temperature (\( T \)), and molecular mass (\( M \)), with support for multiple units and predefined gases. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places for precision.Purpose: Essential for applications in thermodynamics, aerodynamics, and chemical engineering to analyze gas behavior, such as in aircraft design or pipeline engineering.
The calculator derives gas density from the ideal gas law (\( PV = nRT \)), rearranging to:
\( \rho = \frac{MP}{RT} \)
Where:
Available Gases and Molecular Masses:
| Gas | Molecular Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|
| Air | 28.96 |
| Nitrogen | 28.02 |
| Oxygen | 32.00 |
| Carbon Dioxide | 44.01 |
| Methane | 16.04 |
| Custom | User-defined |
Steps:
Gas density is critical for:
Example 1: Calculate the density of air at 1 atm and 20°C, with \( R = 8.31446261815324 \, \text{J/(mol·K)} \), output in kg/m³ and lb/cu ft:
Results:
Example 2: Calculate the density of methane at 100 kPa and 77°F, output in g/L and g/cm³:
Results:
Q: What is gas density?
A: Gas density is the mass of a gas per unit volume, calculated using the ideal gas law, typically in kg/m³ or other units like g/L or lb/cu ft.
Q: How do I choose a gas?
A: Select a predefined gas (e.g., Air) or choose "Custom" to enter a molecular mass.
Q: Why is temperature in Kelvin required?
A: The ideal gas law uses absolute temperature in Kelvin to ensure positive values and accurate calculations.
Q: Does this work for real gases?
A: Yes, for low pressures and high temperatures where ideal gas assumptions apply. For high pressures, real gas models may be needed.
Q: Can I change the universal gas constant?
A: Yes, the default is 8.31446261815324 J/(mol·K), but you can edit it for custom calculations.